Share The Article
What is THC?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sapien turpis condimentum tincidunt integer suspendisse laoreet sed.
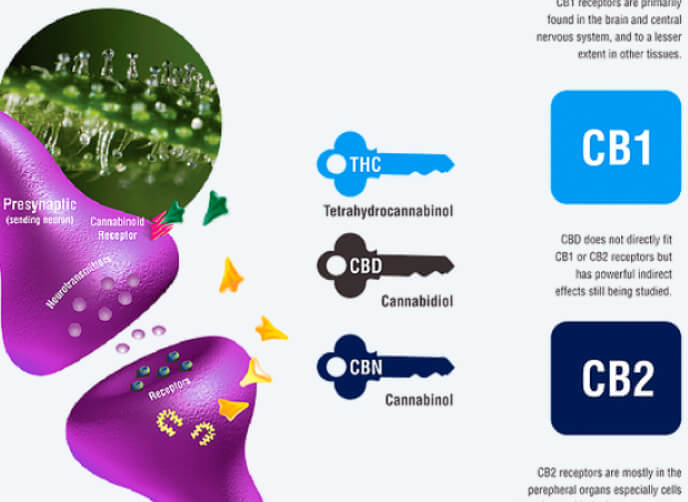
The ECS or Endocannabinoid System is composed out of cell receptors and their adjacent molecules. These receptors act pretty much like locks, as only specific keys can open them up or, in this case, make them react. In anatomy, the keys to these locks are called agonists, which are small chemical molecules capable of triggering a wide range of reactions in the body.
So, each time an agonist meets a receptor cell, it will activate it, but it will also transmit a message as well, letting the receptor know what it has to do.
Thus, when it comes to the ECS, there are two main types of receptors that make its body, and we are talking about Cannabinoid Receptor 1 or CB1 and Cannabinoid Receptor 2 or CB2.
The keys or agonists of these receptors are the endocannabinoids. “Endo” can be translated as “within” and “cannabinoid” makes reference to a compound that is more than suitable for fit within the cannabinoid receptors.
In our body, there are two kinds of endocannabinoids that interest us the most, which are anandamide and 2-Ag. Anandamide was discovered with the help of THC, once this psychoactive component of cannabis was discovered back in the 1960s, by Raphael Mechoulam, an Israeli scientist.
Once THC was discovered, everybody wanted to know what it actually works and if there is a chance for our body to produce the same kind of molecules. It took more than 20 years to find and isolate anandamide.
The name of this endocannabinoid is also interesting as, because they didn’t know how to name it once it was isolated, scientists found the word “Ananda”, in Sanskrit, which means “bliss”. So, yes, anandamides are the so-called “bliss molecules”.